Introduction
Hello there! Do you remember our last conversation about mastering Git? Now, it's time to delve into a more exciting part of your DevOps journey: Linux shell scripting.
Shell scripting is a powerful tool for automating tasks and managing systems, making it an essential skill for DevOps engineers. This guide provides a basic introduction to Linux shell scripting, with a focus on its applications in the DevOps field. Here, we'll cover essential topics to help you get started.
What is Shell Scripting?
Writing Your First Shell Script
Variables and Data Types
Control Flow Statements
Functions
Error Handling
Working with Files and Directories
Networking
DevOps Applications of Shell Scripting
What is Shell Scripting?
Shell scripting is a form of programming that allows you to automate tasks by creating scripts that the shell interprets and executes. In Linux, the most common shell for scripting is Bash, and that's what we'll focus on in this guide.
How to Write Your First Shell Script
To write your first shell script, you need a text editor. You can use popular editors like vi, Vim, or Nano. Here's how to create a simple "Hello, world!" script:
Open your preferred text editor.
Save a new file with the .sh extension, e.g.,
hello.sh.Add the following content to the file:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello, world!"
Save the file.
Make it executable using the following command:
chmod +x hello.sh
- Finally, run the script:
./hello.sh
The script will execute and print "Hello, world!" to the console.
Variables and Data Types
Shell scripts use variables to store data. These variables can hold various data types, including integers, strings, and Booleans. To declare a variable, use the following syntax:
variable_name=value
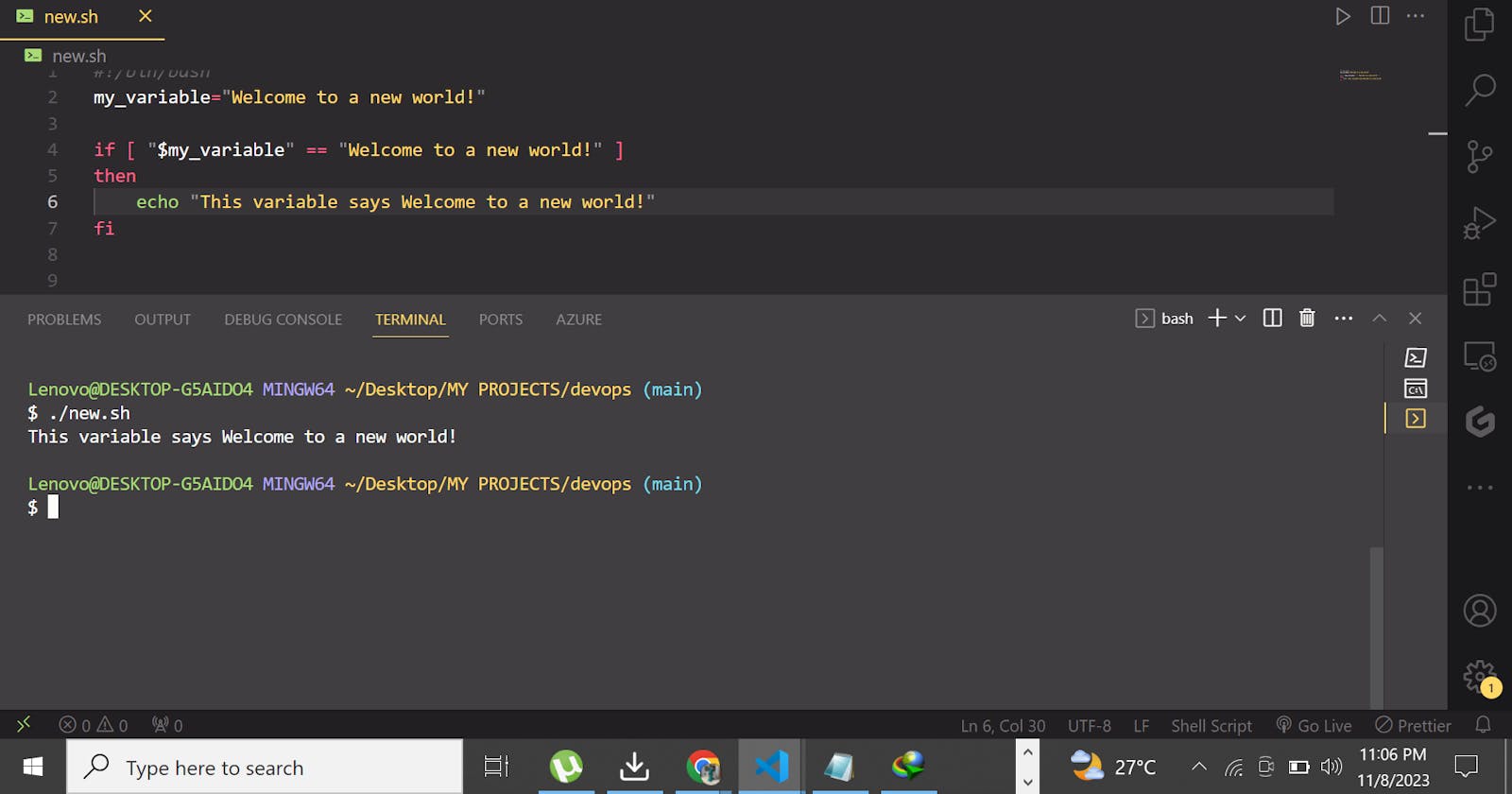
For example, to store the string "welcome to a new world!" in a variable named my_variable, you would write:
To access a variable's value, simply use its name with a $ prefix. For instance, to print the value of my_variable, you would use:
Control Flow Statements
Control flow statements are used to manage the order of execution in shell scripts. The most common ones are:
If Statements:
if condition
then
code_to_execute
fi
For example:
For Loops:
for variable_name in list
do
code_to_execute
done
Example:
While Loops:
while condition
do
code_to_execute
done
Example:
Functions
Functions allow you to group code together for improved modularity and readability. Here's how to define a function:
function function_name() {
# Code to execute
}
For example:
To call a function, simply use its name:
greet
This wraps up our beginner's guide to Linux Shell Scripting for DevOps. Shell scripting is a valuable skill for anyone working in the DevOps field, and with practice and dedication, you can become proficient in automating tasks and managing systems.